LED Grow Lights
the what, the how, the why
LED Technology
LED technology was first invented in the 1950s as a small instrument panel light but only evolved into the high power, low energy lights we see today in the early 2000’s. They can be monochromatic (i.e. single colour) or phosphor coated to emit customised broad spectrum lighting which is ideal for plant growth.
LED grow lights typically start from 9W lamps to 1000W commercial grade lights
Price per watt has fallen significantly over the past 3 years making these lights very affordable
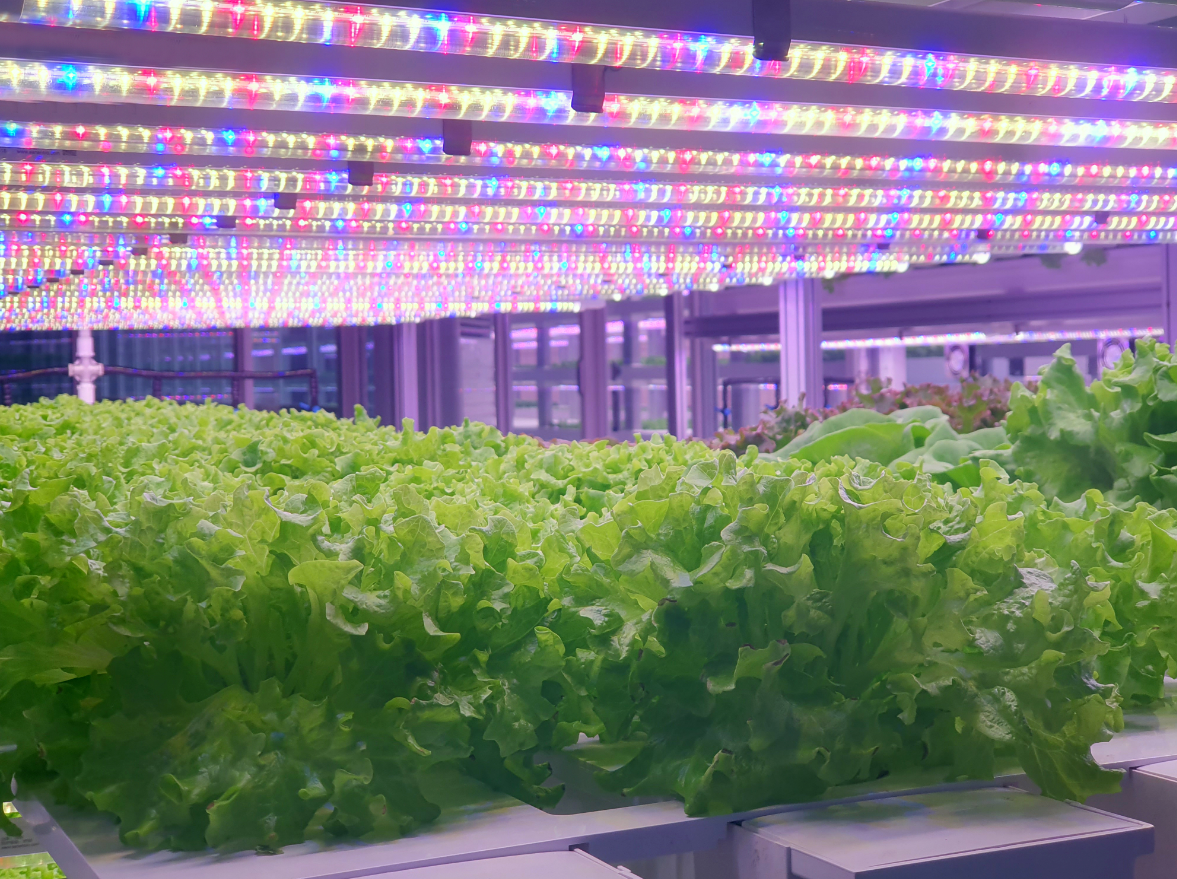

With a significantly higher efficacy from broad spectrum “white” LEDs, the value for money in terms of cost, yield and plant quality makes LEDs the light of choice for many growers.
Higher efficacy results in lower power usage which in turn results in lower heat emission.
All in all LEDs are the present and future of grow lights.
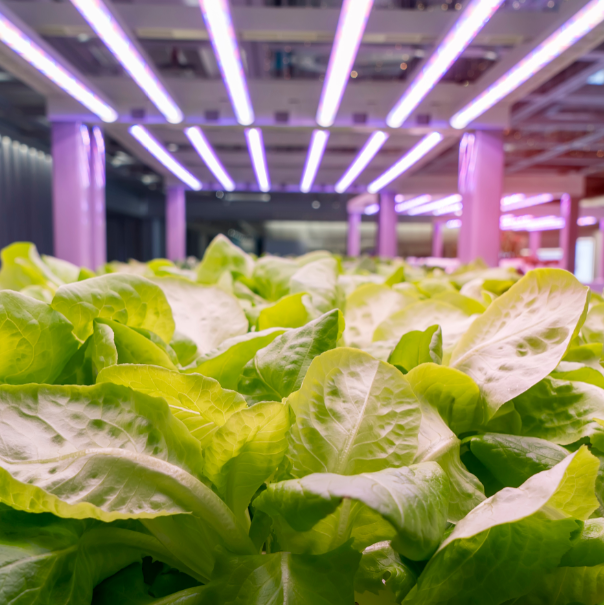
LED Grow Lights
LED grow lights have evolved significantly over the past 10 years and their efficacy is very high
They typically generate in excess of 2.5 µmol/J and range in power from 9W tube lights to 1000W+ top lights
Another very big advantage that LED lighting has over traditional lighting is the spectrum. Broad spectrum (white) LED lights can produce a spectrum that is similar to the PAR spectrum
This allows LED broad spectrum LED lights to be used for all stages of plant growth from germination and propagation, through the vegetative stage and into the flowering stage.


Additional spectra in the upper UV and lower infra red can be added to enhance these areas and additional red 660nm can be added to boost chlorophyll a absorption.
LEDs from different manufacturers have a lot of different nuances and feature and these will be discussed in more detail in this website.
A lot of myths and exaggerated benefits are frequently expressed but we will try to debunk these and reveal the true technical capabilities and upside of LED grow lighting
LEDs are Light Emitting Diodes
Optimal lifespan and LED chip efficacy is obtained by running at reduced power and mounting on an efficient heat sink to draw the heat away from the LED (through the PCB)
The correct balance of forward electrical current from the driver to the LEDs is critical to optimise efficacy and longevity
Actual power used is always 30% to 50% lower than the rated value of the LED chip
Efficacy is spectrum dependent – higher red spectrum = higher efficacy but plants need more than red light
When run at optimal conditions, LED chips are now up to 45% to 70% greater efficacy than HPS
Building LEDs into a fixture reduces efficacy

Secondary lenses for example reduce efficacy by 7% to 10%
The LED driver typically runs between 95% to 97% power factor efficacy
If a supplier claims 600W power for a light that has 600 x 1W LEDs installed, then this is theoretical power and not actual power. Actual power will be closer to 250W to 300W or less.
Always check actual power rating for an LED fixture to understand its true PPF
Passive cooling is more efficient than active (fan) cooling. Fans consume power and reduce the power used for illuminating the LEDs.
Fans can fail which often results in catastrophic and permanent failure of the LED fixture.
What Makes a Good LED Light?
Good quality components ensure goof efficacy and long lifetime
A good light fixture will have top end diodes, will underdrive the diodes, will have effective heat dissipation and will use good quality of components
Efficiency of LED chips varies depending on the colour and construction or “packaging” of the LED chip.
Blue are the most efficient and convert approximately 88% of electrical watts to photon watts
Red convert approximately 69%, far red 66%, and cool white 80%


White LEDs are phosphor coated blue chips
Efficacy of LED chips can now achieve very high numbers.
Blue is typically 3.3 µmol/J, red 3.8 µmol/J, far red 4.0 µmol/J, cool white 3.0 µmol/J whereas HPS is 1.85 µmol/J
Price of lighting fixtures play a part and the use of white LEDs ensure good efficacy, a broad spectrum and a good price.
Relative pricing of LED diodes is in the region of blue x 30, red x 10, far red x 30, cool white x 1
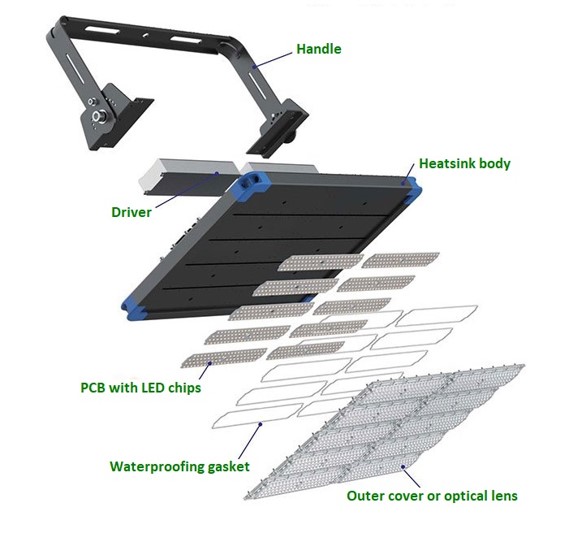
LED Light Construction - Basics
Driver = converts mains AC voltage to low voltage DC
AC = Alternating Current
DC = Direct Current
Heatsink body = draws heat away from the LED chips
Gasket = used to provide IP65 or higher waterproofing
Optics = focuses light toward the plant (can reduce output)
LED Design Process – Useful Light and Uniformity
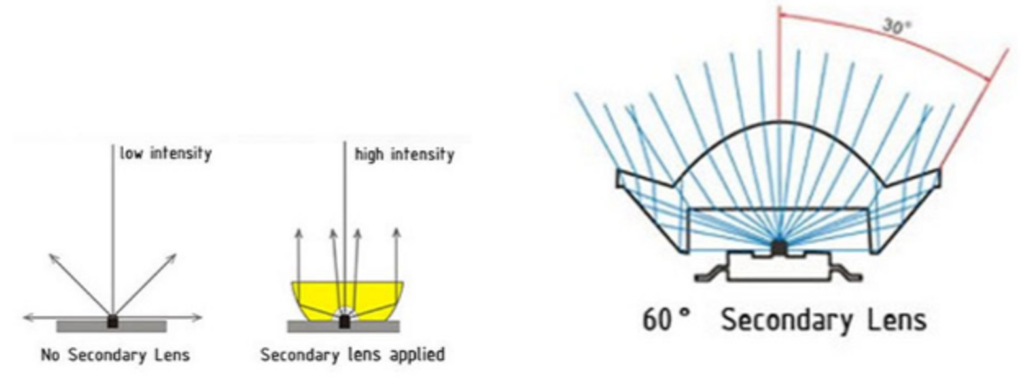
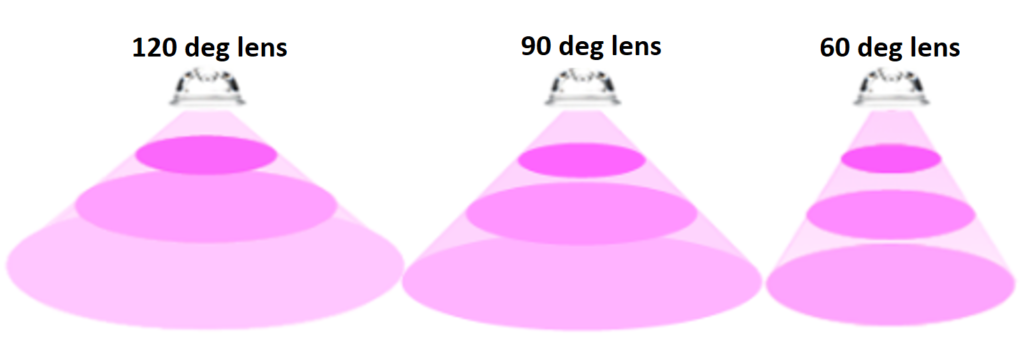
LED systems can use secondary optics to reduce light wastage to the sides and thereby focus maximum light towards the plant
Secondary optics reduce light efficiency by between 7 and 10% but allow the light to be focused where it is required.
Some light systems use wide beam angles that create high PPFD in the centre of the installation but that lose PPFD towards the edges
LED vs HPS
In recent years, the efficiency and price of LED grow lights has ensured that plant growth and plant development can be significantly better for LED lit crops vs HPS lit crops. We have undertaken numerous trials over the years on a variety of different crop types and the results consistently show improved vegetative growth, flowering and yield with LED grow lights compared to HPS.
As explained elsewhere in this website, the conversion of electrical energy to photons of useful light is relatively low in HPS when compared to LED (1.6 µmol/J vs 2.6 µmol/J) resulting in higher heat loads.
The table below shows the relative pros and cons of HPS vs LED .
- 1.6 µmol/J typical
- high energy usage
- high heat load = more cooling needed
- higher transpiration & humidity
- 2.6+ µmol/J typical
- Lower energy use than HPS
- Lower heat produced = better room climate
- better spectrum and crop quality
F.A.Q.
if you cannot find the answer to your question then please send via contact page
Modern, commercial grade LEDs grow lights that consume 600W power draw and perform at 2,5 umol/m2/s or higher emit similar light levels to a 1000W HPS.
This depends on the type of plant you are growing but generally speaking, a tomato crop can, for example, now achieve in excess of 30 kg /sqm under LED compared to 22 kg / sqm under HPS.
Some suppliers claim their LED grow lights are high wattage but in reality, they are referring to the theoretical maximum rating of the LED chips rather than the real power usage. A light that draws 100W in power will be equivalent to a 150W HPS assuming it has high efficacy.
When suppliers quote 50,000 hours on their marketing data they are actually referring to the predicted light drop off over this period of time rather than the lifetime warranty of the fixture. If the fixture has poor heat dissipation, uses poor quality chips and driver, then it will fail within a couple of years. Good quality LED fixtures manufactured using good design, good components and good quality control will last 5 years or more.
Your grow room uses water for irrigating the plants and the atmosphere has high humidity. Water and electrics are not a great mix. I would recommend buying a waterproof LED grow light.
